

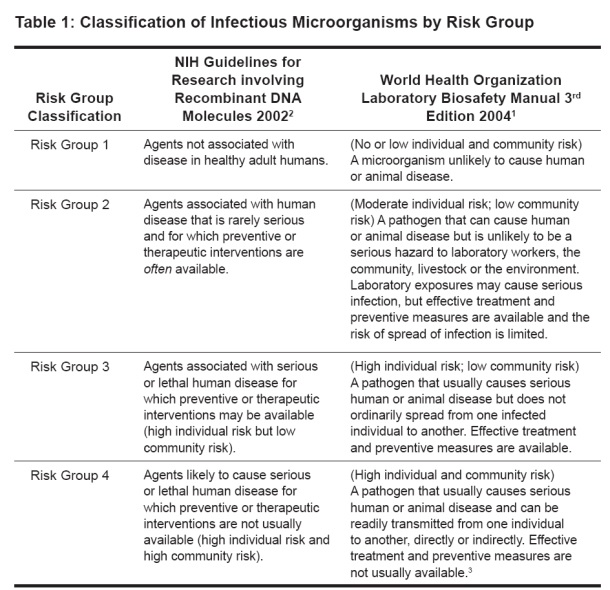
Risk assessment is an important responsibility for directors and principal investigators of microbiological and biomedical laboratories. Institutional biosafety committees (IBC), animal care and use committees, biological safety professionals, and laboratory animal veterinarians share in this responsibility. Risk assessment is a process used to identify the hazardous characteristics of a known infectious or potentially infectious agent or material, the activities that can result in a person's exposure to an agent, the likelihood that such exposure will cause a LAI, and the probable consequences of such an infection. The information identified by risk assessment will provide a guide for the selection of appropriate biosafety levels and microbiological practices, safety equipment, and facility safeguards that can prevent LAIs.

Principles of Biosafety
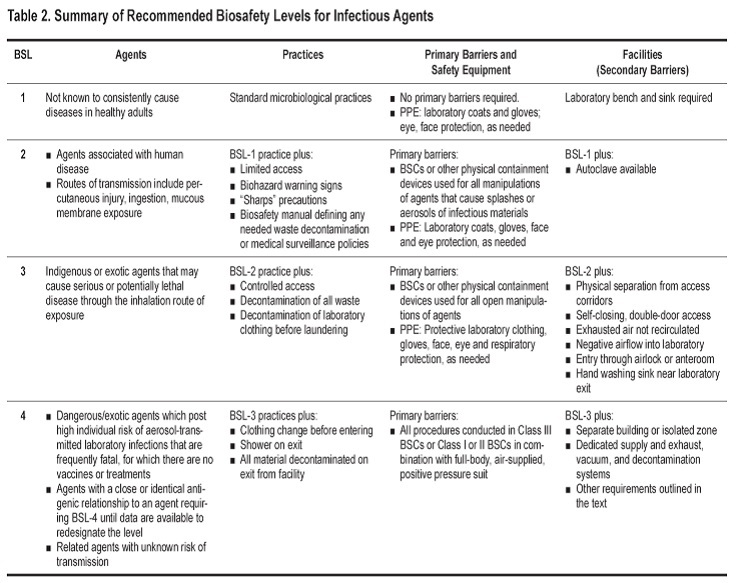
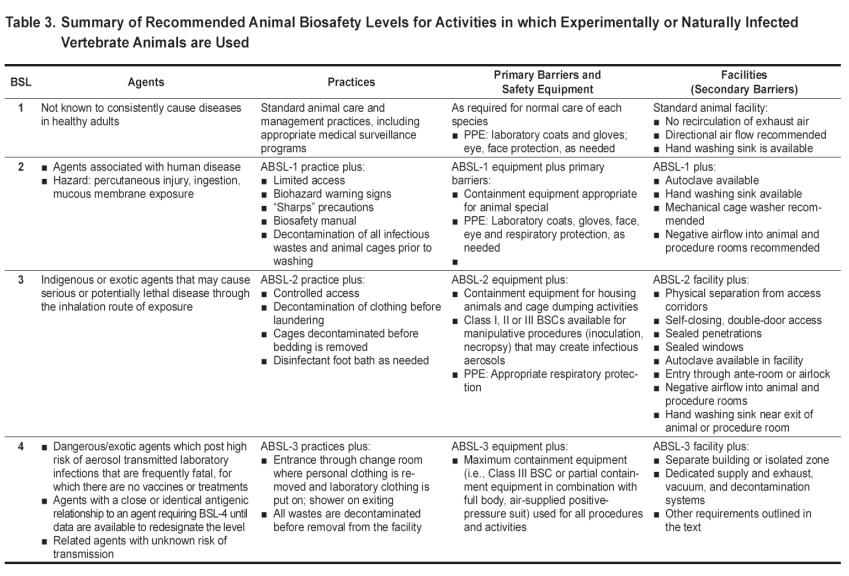
A fundamental objective of any biosafety program is the containment of potentially harmful biological agents. The term "containment" is used in describing safe methods, facilities and equipment for managing infectious materials in the laboratory environment where they are being handled or maintained. The purpose of containment is to reduce or eliminate exposure of laboratory workers, other persons, and the outside environment to potentially hazardous agents.The use of vaccines may provide an increased level of personal protection. The risk assessment of the work to be done with a specific agent will determine the appropriate combination of these elements.
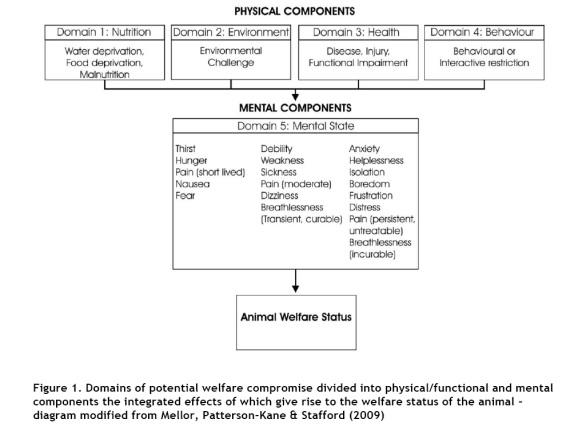

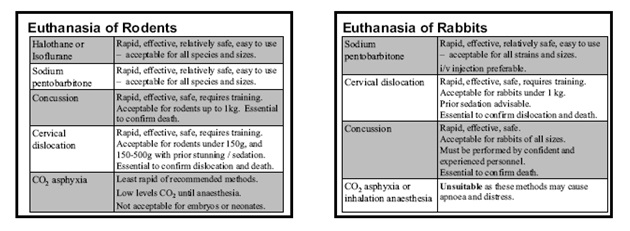
Principle of 3R in animal experimentation: Replace, Reduce and refine the animal use for experimentation.

